Cloud Deployments and AWS (Amazon Web Services) Core services
☁️👨💻
NOTE: Check core services section for a brief info of the pertaining AWS service
What are you architecting for?
Categories:
- Lift & shift
Third-party software; one just needs to deploy it
- Modernization
Leverage some components like database on the cloud
- Extension of on-prem
New component to be served on the cloud that interacts with an on-prem setup through APIs
- Green-field
A completely new software from the ground up
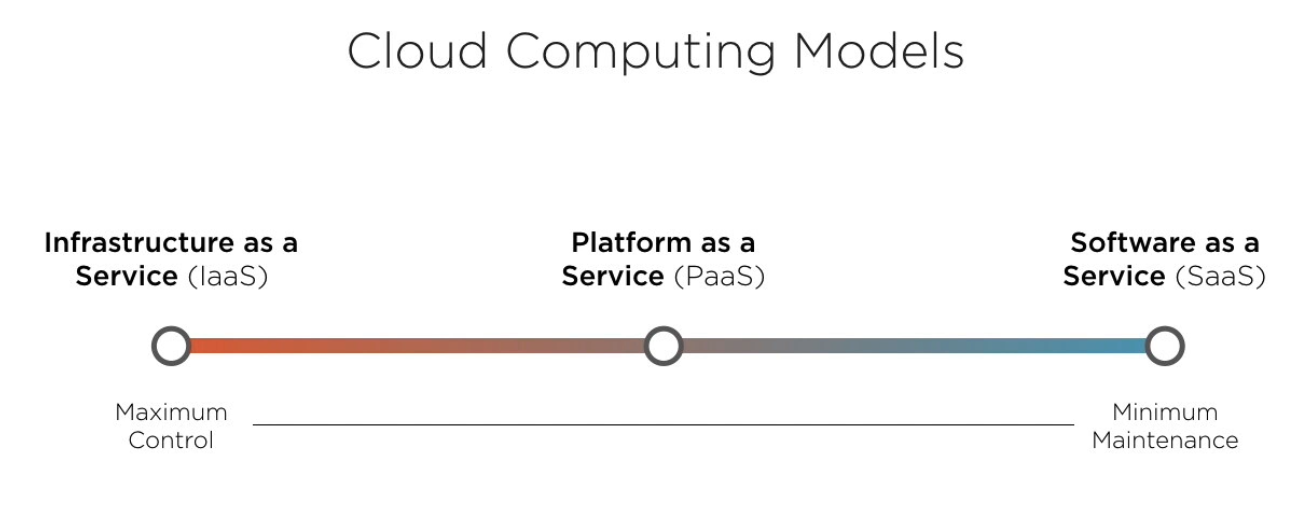
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS?
DevOps
- CI/CD
- Monitoring and logging
- Configuration management
Puppet/chef, software, OS upgrades
Sample steps to follow for IaaS
infra
- Use CloudFormation designer tool and deploy necessary services
- Use OpsWorks for configuration management
- Configure monitoring and a centralized logging solution
Can use third-party, open source or CloudWatch for that
deployment
- Create an EC2 AutoScaling resource group for HA
Auto scaling can be configured based on these parameters:
- Average CPU % utilization
- Average network in
- Average network out
- Load balancer requests per target Policies should also be configured properly. When to scale out and scale in. Performance testing is critical
- Configure an HTTPS/HTTP/TCP load balancer and put it in front of this setup (AWS ELB)
- Global Accelerator configuration
Based on the resources one has allocated in availability zones
- Allocate an elastic IP and integrate it with Route 53
AWS Core services
1. Interacting with AWS
- Web console
- CLI
Access keys required. Root user keys can also be retrieved but IAM user with limited permissions is recommended.
- AWS SDK for automation
All major languages are supported
2. Compute Services
Leverage cloud-based virtual machines for workloads.
- EC2*
Secure and resizable virtual servers Generally used in autoscaling resource groups
- Elastic Beanstalk
Scaling and deploying web apps and services
- AWS Lambda
Compute without managing servers. "Serverless".
- Step functions
Orchestration of workflows through a fully managed service. Can integrate with Lambda, DynamoDB, Data processing services and ML services just to name a few.
It's advised that one creates related services into a single resource group for isolation and easier management.
2A. EC2 concepts
- Instance types
General purpose, Memory optimized, storage optimized, Accelerated computing
eg. t3.medium, m5.large, c5d.24xlarge, p3.16xlarge - Root disk type
Two types: 1. Instance store (ephemeral store) | 2. Elastic Block Storage: EBS (Persistant storage)
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
There's a marketplace to select an AMI or an org can have a custom AMI
- Purchase options
Out of scope of this article, one needs to have a complete idea about the workload that will be scheduled on these EC2 instances.
While launcing, we can provide commands to run during boot process, server tags to locate it properly. Security related configs can be applied as well, who all can access the instance, what type of connections to be allowed, etc
2B. Elastic Beanstalk concepts
Automates the process of deploying and scaling workloads on EC2 (PaaS). We only pay for the services we use
What Elastic Beanstalk has over EC2?
- Monitoring
- Scaling
- Deployment
- Customization
It's app specific instead of server specific.
2C. AWS Lambda
Primary service for serverless architecture
- Enables event-driven workflows
- Enables running code without provisioning infrastructure
- Charged for usage based on execution time
- Reduced maintainance requirements, AWS does that for you
- Scales based on demand
Networking and Content Delivery Services
- VPC: Virtual Private Cloud* and Direct Connect
VPC: Can configure private (NAT) and public subnets. Can peer with other VPCs
Direct Connect: dedicated network connection from own data center to AWS - DNS with Route 53*
Global, Highly Available with failover DNS One can configure internet facing infrastructure as well as the intranet
- ELB: Elastic Load Balancing* and scaling
AWS offers both HTTP/HTTPS and TCP load balacing Integrates with EC2, ECS and Lambda Everything is customizable including healthchecks, ports, connection scheme, etc. Kind of like NGINX plus
- CloudFront and API Gateway
CloudFront: CDNs with edge locations, closest servers, static and dynamic content can be served API Gateway: Fully managed API management service. Directly integrates with multiple AWS services, leverages CloudFront.
- Global Accelerator
Routes traffic through AWS internal network. Similar to CloudFront but needs static IP addresses to serve content. Can be also placed in front of ELB instances load balancing their own availability zones. Multiple resource groups/IPs can be targetted I can configure say, 80% of the traffic to go in AZ and 20% in other
File storage services
- S3*
Stores files as objects in
buckets. Different storage classes for different use cases. URL access possible so it's possible to serve static websites. Configurable rules for data lifecycle: data objects inside buckets can be transitioned into different storage class based on time, similar thing with object deletion. Use S3 transfer acceleration for quick uploads using CloudFront. - S3 Glacier and Glacier Deep
Archiving data within S3 as a separate storage class. Configurable retrieval times.
- EBS (Elastic Block Store)
Persistant block storage for EC2 instances. Allows snapshoting. Multiple volume types: SSD, IOPS SSD, HDD, Throughput optimized HDD
- Elastic File System
NFS file system. Configurable data lifecycle rules. Multiple availability zones supported.
- AWS Snowball | Snowmobile
Physical devices for data transfer. Snowmobile is an extreme version of Snowball. AWS provides the device, end-users upload their data into this device and then data is uploaded onto S3.
Databases and utilities
IaaS
- Launch a database on EC2 for complete control
PaaS
- Relational Database Service (RDS)
MySQL, Postgres, MariaDB, AWS Aurora Provisioning, patching, backing and recovery Launches into a VPC DMS: Data Migration Service to onboard on-prem DB onto RDS
SaaS
- DynamoDB
NoSQL. Provides both key-value and document database. Elastic as per scale. In-memory cache also supported
- ElastiCache and Redshift
ElasticCache: In-memory data stores. Supports both memcached and Redis. DB layer caching and Session storage can be done. Redshift: Data warehousing. High-performance disks and columnar storage. Isolation with VPC.
Management and governance services
- CloudTrail
Log, monitor and retain account activity. auditlog, basically. Inserts this trail in S3 or CloudWatch logs.
- Tracking with CloudWatch* and Config
CloudWatch: Metrics, logs and alarms. (just like Grafana) Config: continuously checks if the infrastructure is tweaked from its desired state
- Systems Manager
UI for ops data. Automate operational tasks through this.
- CloudFormation
Infrastructure as a Code: Provisions infrastructure (EC2 instances, S3, lambda, etc) based on declarative templates, if the stack is same. Comes with a drag-n-drop desginer tool to diagrammatically create the whole infrastructure
- OpsWorks
Managed instances of Chef and Puppet
- Organizations and Control Tower
Organizations: Account management, consolidated billing, auditing, etc Control Tower: Create user accounts with templates